Finding open ports using Rust's fearless concurrency
I've been using nmap for quite some time and wanted to create something similar (albeit much simpler) using Rust. This page details the creation of an asynchronous multi-threaded port scanner that allows the user to specify how the scan should run using command line arguments.
- I've used the clap crate (Command Line Argument Parser) to easily parse and store command line arguments.
-
A user must specify the target IP address to scan using the
-tor--targetflags followed by the IP address. -
A user may pass the
-v or --verbosityflag to set the output level to errors only, informational, or full trace level. If this flag is not set, the program will default to error output only (Save for the relevant port information printed at the end of the program's execution). -
A user may pass the
-n or --threadsflag to specify how many threads should run concurrently. This should ideally match the number of cores on a user's CPU. It will default to 4 if this flag isn't set. -
A user may pass the
-p or --port-rangeflag in order to specify the ports to scan. This can take the form of one or more ranges (1:1024) or a comma separated list (80, 443) or a combination of both. The default is ports 1 through 1024. -
A user may pass the
-m or --timeoutflag to specify how long a connection should be attempted on each port before timing out (in millisconds). The default is 100 ms. -
A user may supply the
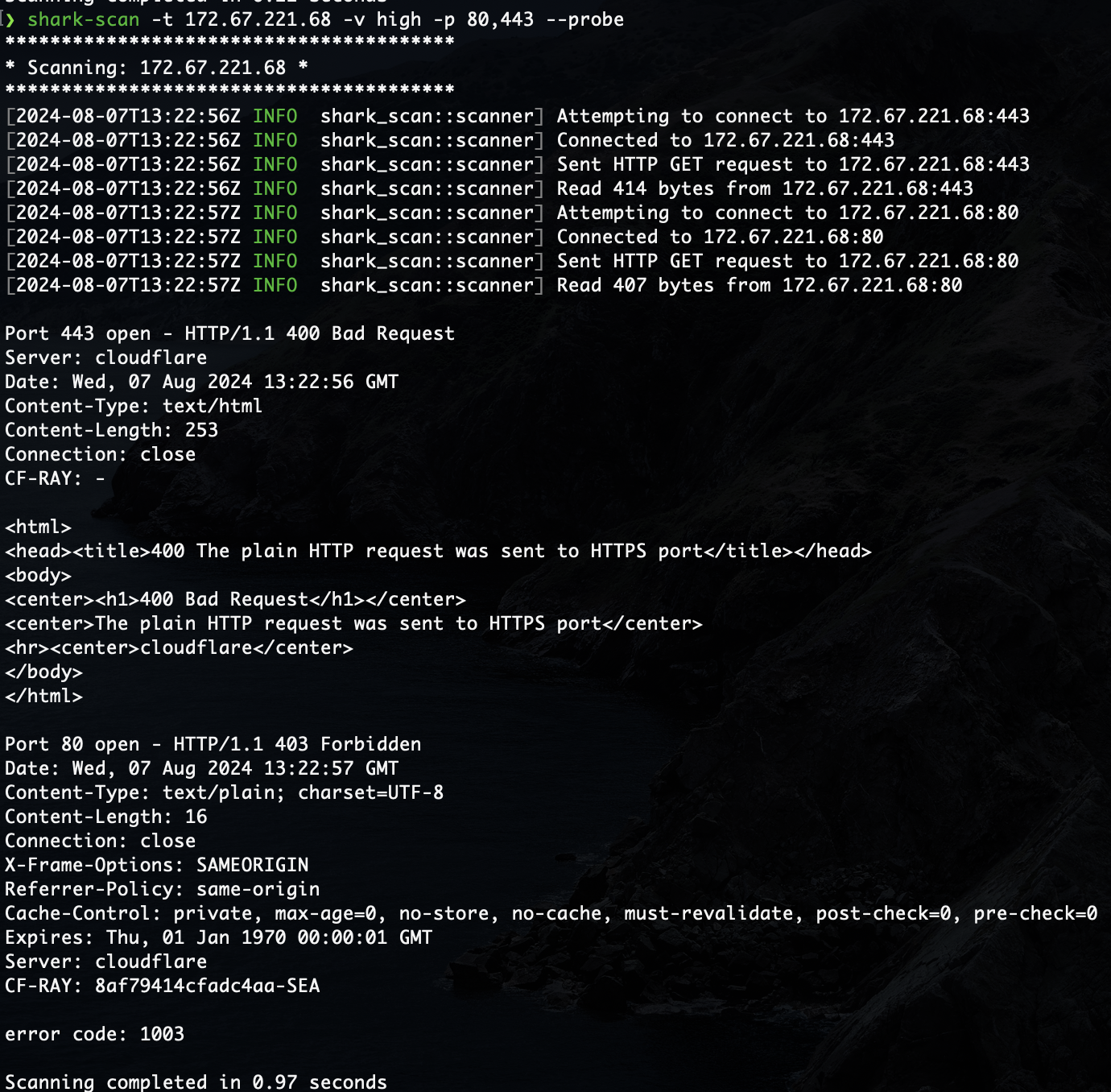
--probeflag in order to send an HTTP GET request to any open ports and read the response from the service operating at that port. This won't work on any services not using HTTP, and may present a security risk if the host sends a malicious response. -
The
parse_ports()function expects a string describing the ports to scan, this string is the value either provided after using the-p or --port-rangeflag or else the default value of1:1024. - The function splits the string at any comma characters, trimming any whitespace, and adds these numeric values to a vector of ports to scan. If port ranges (1:5) are encountered, these will be expanded and added to the vector (1, 2, 3, 4, 5).
-
Calling
panic!directly or using methods that result in a panic is usually discouraged, but in the context of this program it makes no sense to continue if valid ports are not specified. - The vector of ports will be returned by the function.
- I've written some tests to cover the expected functionality of this function.
use clap::Parser;
#[derive(Parser, Debug)]
#[command(author, version, about, long_about = None)]
pub struct Args {
/// The target IP address to scan
#[arg(short = 't', long)]
pub(crate) target: String,
/// The verbosity level (none, low, high)
#[arg(short, long, default_value = "none")]
pub verbosity: String,
// The number of threads to use
#[arg(short = 'n', long, default_value = "4")]
pub(crate) threads: usize,
/// The port range to scan in the format start:end or comma separated
#[arg(short = 'p', long, default_value = "1:1024")]
pub(crate) port_range: String,
/// The time in milliseconds to await successful port connection
#[arg(short = 'm', long, default_value = "100")]
pub(crate) timeout: u64,
/// ***Do not use against untrusted hosts***
/// Probe the socket by performing an HTTP GET request
#[arg(long)]
pub(crate) probe: bool,
}
pub(crate) fn parse_ports(port_arg: &str) -> Vec {
let mut ports = Vec::new();
for port in port_arg.split(',') {
let port = port.trim();
if port.contains(':') {
let range: Vec<&str> = port.split(':').collect();
if range.len() == 2 {
let start: u16 = range[0].parse().expect("Invalid start port, expected similar to -p 1:1024");
let end: u16 = range[1].parse().expect("Invalid end port, expected similar to -p 1:1024");
for port in start..=end {
ports.push(port);
}
} else {
panic!("Bad port range. Expected similar to -p 1:1024");
}
} else {
let port: u16 = port.parse().expect(&format!("Invalid port: {}", port));
ports.push(port);
}
}
ports
}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::parse_ports;
#[test]
fn test_parse_ports() {
let port_range = "20:25,31,32,45:50";
let ports = parse_ports(port_range);
assert_eq!(ports, vec![20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 31, 32, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50]);
}
#[test]
fn test_parse_ports_list_trimmed() {
let port_range = "14, 15, 29";
let ports = parse_ports(port_range);
assert_eq!(ports, vec![14, 15, 29]);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic(expected = "Invalid port:")]
fn test_parse_invalid_port_range() {
let port_range = "14-15";
let _ = parse_ports(port_range);
}
#[test]
#[should_panic(expected = "Invalid port:")]
fn test_parse_invalid_port_value() {
let port_range = "14, a2";
let _ = parse_ports(port_range);
}
}
Implementing the scanning logic
- This logic makes extensive use of tokio methods and data structures. Tokio is an asynchronous runtime for Rust that provides data structures and methods that are safe to use not only in an async context but also safe to use across multiple threads.
-
A
ScanResultstruct is defined to contain information about ports scanned. Thebannermember will only be used then the--probeflag is used. -
The
probe()function is used to obtain information regarding an open port. Right now it only performs an HTTP GET request which in practice will only return information on Port 80. if other ports are running services that use HTTP this function may receive useful information. -
The
check_port()function is used to test every specified port to see if it will complete a TCP connection. -
The
scan()function prints some helpful info tostd::outand spawns a specific number of threads to callcheck_port()on specific ports. Program execution time and open ports are ultimately printed tostd::out. -
I've written some tests to check expected functionality of the
check_port()function.
use std::io;
use tokio::net::TcpStream;
use tokio::time::timeout;
use tokio::sync::Mutex as AsyncMutex;
use std::time::{Duration, Instant};
use std::sync::{Arc};
use threadpool::ThreadPool;
use log::{error, info};
use serde::{Deserialize, Serialize};
use tokio::io::{AsyncReadExt, AsyncWriteExt};
use crate::{parser::{parse_ports, Args}};
/// A struct to contain scan results for a given port:
///
/// `status` will be set to open if a connection succeeds
///
/// If the --probe flag is used, `banner` will contain the first 1024 bytes
/// returned by the service on that port, if it supports HTTP
#[derive(Serialize, Deserialize)]
pub struct ScanResult {
port: u16,
status: String,
banner: Option<String>,
}
async fn probe(target: &str, port: u16, timeout_ms: u64) -> Option<String> {
let address = format!("{}:{}", target, port);
info!("Attempting to connect to {}", address);
match timeout(Duration::from_millis(timeout_ms), TcpStream::connect(&address)).await {
Ok(Ok(mut stream)) => {
info!("Connected to {}", address);
let http_request = format!(
"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: {}\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n",
target
);
match stream.write_all(http_request.as_bytes()).await {
Ok(_) => info!("Sent HTTP GET request to {}", address),
Err(e) => {
error!("Failed to send HTTP GET request to {}: {:?}", address, e);
return None;
}
}
let mut banner = vec![0; 1024];
// Wait one full second to read response from server
match timeout(Duration::from_secs(1), stream.read(&mut banner)).await {
Ok(Ok(n)) if n > 0 => {
info!("Read {} bytes from {}", n, address);
return Some(String::from_utf8_lossy(&banner[..n]).to_string());
}
Ok(Ok(_)) => {
error!("No data read from {}", address);
}
Ok(Err(e)) => {
error!("Failed to read from {}: {:?}", address, e);
}
Err(_) => {
error!("Read operation timed out for {}", address);
}
}
}
Ok(Err(e)) => {
error!("Failed to connect to {}: {:?}", address, e);
}
Err(_) => {
error!("Connection attempt timed out for {}", address);
}
}
None
}
async fn check_port(target: Arc<String>, port: u16, timeout_ms: u64, do_probe: bool, results: Arc<AsyncMutex<Vec<ScanResult>>>) {
let address = format!("{}:{}", target, port);
match timeout(Duration::from_secs(timeout_ms), TcpStream::connect(&address)).await {
Ok(Ok(_)) => {
if do_probe {
let banner = probe(&target, port, timeout_ms).await;
let mut results = results.lock().await;
results.push(ScanResult {
port,
status: "open".to_string(),
banner,
});
} else {
let mut results = results.lock().await;
results.push(ScanResult {
port,
status: "open".to_string(),
banner: None,
});
}
}
Ok(Err(e)) => {
let status = match e.kind() {
io::ErrorKind::ConnectionRefused => "refused",
_ => "failed",
};
info!("Port {} {}", port, status);
}
Err(_) => {
info!("Port {} timed out", port);
}
}
}
pub async fn scan(args: Args) {
let ports = parse_ports(&args.port_range);
let target = Arc::new(args.target.trim().to_string());
println!("{}", "*".repeat(40));
println!("* Scanning: {} *", target);
println!("{}", "*".repeat(40));
let start = Instant::now();
let pool = ThreadPool::new(args.threads);
let results = Arc::new(AsyncMutex::new(Vec::new()));
for port in ports {
let results = Arc::clone(&results);
let target = Arc::clone(&target);
let timeout = args.timeout;
let probe = args.probe;
pool.execute(move || {
let rt = tokio::runtime::Runtime::new().unwrap();
rt.block_on(async move {
check_port(target, port, timeout, probe, results).await;
});
});
}
pool.join();
let end = Instant::now();
let duration = end.duration_since(start);
let results = results.lock();
println!();
for result in results.await.iter() {
println!("Port {} {}{}", result.port, result.status,
result.banner.as_ref().map(|b| format!(" - {}", b)).unwrap_or_default());
}
println!("\nScanning completed in {:.2} seconds", duration.as_secs_f64());
}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use super::*;
#[tokio::test]
async fn test_open_port() {
// Assuming the local network has port 80 open
let target = Arc::new("192.168.1.1".to_string());
let port = 80;
let results = Arc::new(AsyncMutex::new(Vec::new()));
let results_clone = Arc::clone(&results);
check_port(target, port, 100, false, results_clone).await;
let results = results.lock().await;
assert_eq!(results.len(), 1);
assert_eq!(results[0].port, port);
assert_eq!(results[0].status, "open");
}
#[tokio::test]
async fn test_closed_port() {
// Assuming the local network has port 90 closed
let target = Arc::new("192.168.1.1".to_string());
let port = 90;
let results = Arc::new(AsyncMutex::new(Vec::new()));
let results_clone = Arc::clone(&results);
check_port(target, port, 100, false, results_clone).await;
let results = results.lock().await;
assert_eq!(results.len(), 0);
}
}
Configuring logging level and parsing arguments in main()
-
Methods from the clap crate are used to parse command line arguments that will be read
in the
scan()function. - The verbosity arguments is used to configure the logging level for the program's execution.
-
scan()is invoked in an async context.
use clap::{CommandFactory, FromArgMatches};
use log::LevelFilter;
use shark_scan::{parser::Args, scanner::scan};
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() {
let command = Args::command().arg_required_else_help(true);
let matches = command.get_matches();
let args = Args::from_arg_matches(&matches).expect("Failed to parse arguments");
match args.verbosity.as_str() {
"none" => env_logger::builder()
.filter_level(LevelFilter::Error)
.init(),
"low" => env_logger::builder().filter_level(LevelFilter::Info).init(),
"high" => env_logger::builder()
.filter_level(LevelFilter::Trace)
.init(),
_ => env_logger::builder()
.filter_level(LevelFilter::Error)
.init(),
}
scan(args).await;
}
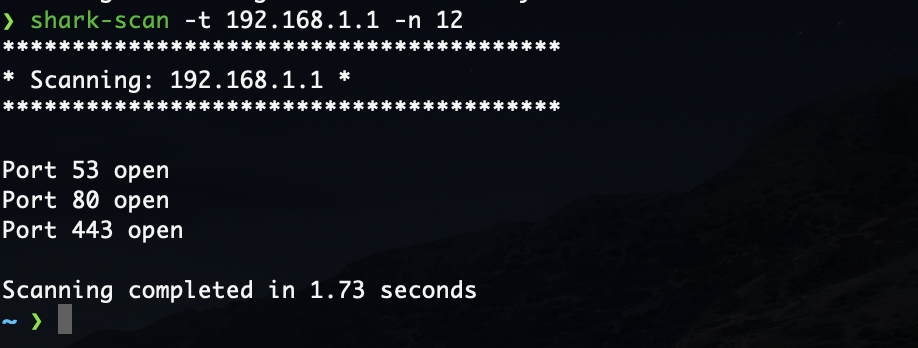
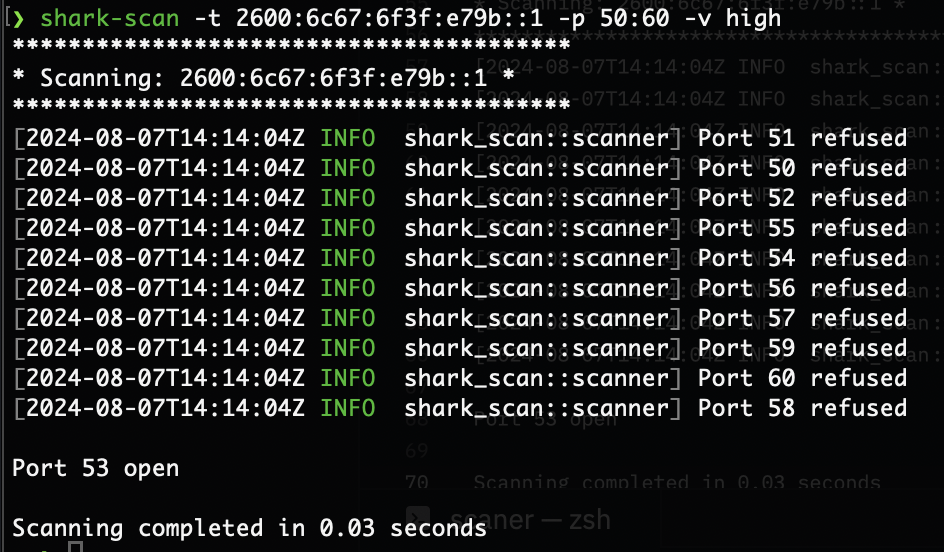
Examples of usage